-
ENGLISH

- ENGLISH
- JAPANESE
-
Copyright(C)SaeMah. All right reserved
Mooring wire rope is a high-strength steel rope designed to safely secure vessels during mooring operations. It offers excellent tensile strength and durability, withstanding extreme loads and friction in harsh marine environments, ensuring long-term stable performance.
Saemah Wire Rope is satisfied JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), and is supplied with Class Certificate(NK, Lloyd and ETC.)
Quotefrom OCIMF 3rd Edition
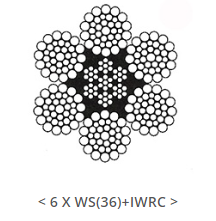
A line should be selected that combines theproper attributes for mooring when reasonable flexibility and high MBL arepriority requirements. The recommended construction is 6x36 or 6x41 (6x36class) with the wires in each strand of equal lay and the stands of regular(ordinary) right hand lay.
Steel wire lines with and independent WireRope Core (IWRC) are strongly recommended over fiber core steel wire lines forseveral reasons. And IWRC steel wire line has a much greater resistance tocrushing, higher MBL for a given diameter and greater strength retention whenbent.
Construction
6 X 36 OR 6X41 (6 X 36 Class) wireconstruction is recommended for all general mooring line applications with thewires in each strand of equal lay and the strands of regular(ordinary)righthand lay according to OCIMF 4th Edition.

-Every vessel shall have Ship Design MBL.
-Every vessel shall implement LineManagement Plan (LMP)
New regulations and guidelines
The IMO Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) hasissued new requirements related towing and mooring equipment. The requirementsare incorporated in the amendments to SOLAS Regulation II-1/3-8 and will comeinto force on 1 January 2024.
• IMO MSC.1/Circ.1175/Rev.1, “Guidance on shipboard towing and mooring equipment”
This circular has been updated to nowinclude a reference to the calculation of the Ship Design Minimum Breaking Load(SDMBL). The update will apply to all vessels constructed after January 2024.The original document remains in effect for vessels built between January 2007and January 2024, and is not replaced by the revised version.
• IMO MSC.1/Circ.1619, “Guidelines on the design of mooring arrangements and theselection of appropriate mooring equipment and fittings for safe mooring”
These guidelines are applicable to allvessels constructed on or after 1 January 2024 and offer details on the designof mooring systems as well as the selection of mooring equipment, includinglines.
• IMO MSC.1/Circ.1620, “Guidelines for inspection and maintenance of mooringequipment including lines”
These guidelines are applicable to allvessels and provide guidance on the inspection and retirement of mooring lines,along with the criteria for replacing lines after their retirement.
Keydefinitions
|
Ship Design MBL (MBLSD, SDMBL) |
Ship Design Minimum Breaking Load. The minimum breaking load of new, dry, mooring lines for which shipboard fittings and supporting hull structures are designed in order to meet mooring restraint requirements.
|
|
LDBF |
Line Design Break Force. The minimum force that a new, dry, spliced mooring line will break at. (Wet for only nylon) 100-105% of SDMBL
|
|
TDBF |
Tail Design Break Force. The minimum force that a new, wet, spliced mooring tail will break at. 125-130% of SDMBL
|
|
WLL |
This is the maximum load that a mooring line should be subjected to in operational service, calculated from the standard environmental criteria. Steel wire rope : 55% of SDMBL / Synthetic rope: 50% of SDMBL
|
|
D/d |
The diameter, D, of a mooring fitting divided by the diameter, d, of a mooring line that is led around or through the fitting. The D/d ratio is used by mooring line manufacturers to specify the minimum radius of a fitting around or through which a mooring line of diameter "d" should be led, in order to reduce or mitigate bend loss of strength of the mooring line.
|
All ships are required to keep the LMP including;
1. Procedures for mooringoperation, inspection and maintenance of mooring equipment including mooringlines. 3.1 (3.1. Safe use of mooring equipment and fitting)
2. Procedures to allow theidentification and management of mooring lines, tails and associatedattachment. 3.3 (3.3. Control of mooring lines)
3. Manufacturers’ criteria formooring line replacement. 4.3.1 (4.3.1. Replacement of in-service mooringlines)
4. Records of mooring equipmentinspections and maintenance, and mooring line inspections and replacement.4.4.3 / 6.1 (4.4.3. Records of inspection and maintenance of equipment andfittings should be available on board. & 6.1. Records of inspection andmaintenance of mooring equipment and inspection and replacement of mooringlines)
5. Manufactures’ test certificatesfor mooring lines, joining shackles and synthetic tails. 6.2 (6.2 Certificate)
6. Records of the original mooringdesign concepts, equipment, arrangements and specifications. 4.4.4 (4.4.4.Records of original design concept, equipment, arrangement and specification.)

There is a problem with the server and network.
Please contact us separately.
Please do not close the window and wait a moment.

We will respond shortly.
Thank you for visiting.